World
What is a Liability, Examples, Types, its Placement, etc?
- April 13, 2018
- Posted by: Ahuja Sahil
- Category: Liabilities
Liability – Accounting Definition
In a business scenario, a liability is an obligation payable to a third party. It may or may not be a legal obligation and arises from transactions and events that occurred in the past. It is usually payable to an external party (e.g. lenders, long-term loans).
There are mainly three types of liabilities except for internal liabilities. Current liabilities, Non-Current liabilities & Contingent Liabilities are the three main types of liabilities. The settlement of liability is expected to result in an outflow of funds from the company.
“Total Liabilities” are always equal to “Total Assets”.
(Capital + Liabilities) = Assets
Accounting for a Liability Account
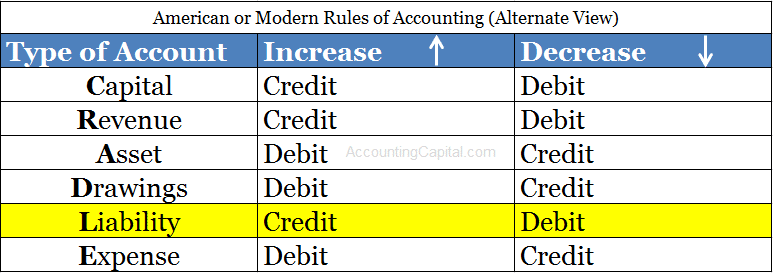
While dealing with a liability account it is important to know that it would always carry a credit balance.
As per the modern classification of accounts or American/Modern Rules of accounting an increase in liability is credited whereas a decrease is debited.
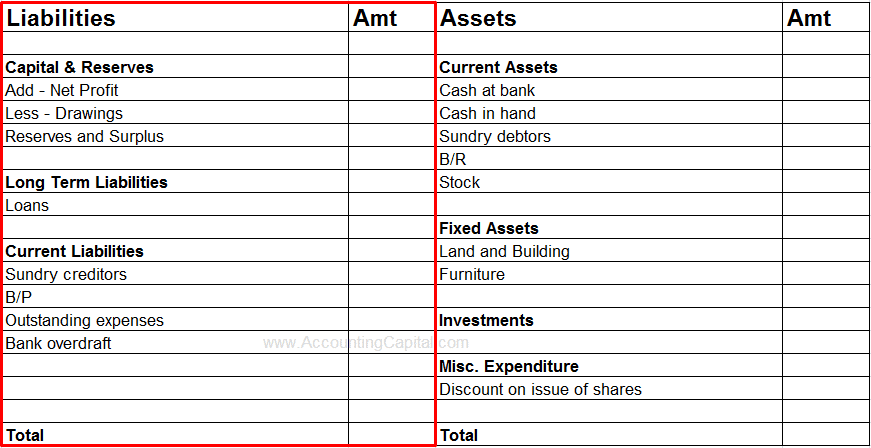
Liabilities Shown in Financial Statements
Liabilities are shown on the left-hand side of a vertical balance sheet. They would always equal to the assets of a company. This is the reason why a balance sheet always tie-up.
Types of a Liability
1. Current Liabilities – Also known as short-term liabilities they are payable within 12 months or within the operating cycle of a business. Examples – trade creditors, bills payable, outstanding expenses, bank overdraft etc.
2. Non-current Liabilities – Also termed as fixed liabilities they are long-term obligations and the business is not liable to pay these within 12 months. Examples – long-term loans, bonds payable, debentures, etc.
3. Contingent liabilities – are liabilities that may come into existence depending on the outcome of a future occurrence. In case the event does not happen, an organization is not liable to pay anything. They are shown as a footnote to the balance sheet. Examples of contingent liabilities are
- Lawsuit proceedings
- Product warranty claims
- Guarantee for loans
4. Owner’s funds/Capital/Equity – Last among types of liabilities is the amount owed to proprietors as capital, it is also called owner’s equity or equity.
Internal and External Liabilities
Internal – It is payable to internal parties such as promoters (owners), employees etc. Example – Capital, Salaries, Accumulated profits, etc.
External – It is payable to external parties such as lenders, vendors, etc. Example – Borrowings, Creditors, Taxes, Overdraft, etc.
Short Quiz for Self-Evaluation
Your quiz has been submitted
Want to re-attempt? - Simply “refresh” this page.
Please check out more content on our site :)
Subscribed? - Check your mailbox
Thank You!
We faced problems while connecting to the server or receiving data from the server. Please wait for a few seconds and try again.
If the problem persists, then check your internet connectivity. If all other sites open fine, then please contact the administrator of this website with the following information.
TextStatus: undefined
HTTP Error: undefined
Some error has occured.
>Related Long Quiz for Practice Quiz 17 – Contingent Liabilities
>Read Contra Liabilities